Function and Application of Automobile Fuse
What are car blade fuses and their functions? Abbreviation: Vehicle fuses
Automotive fuses protect the circuits protected by them from impermissibly high currents, which are caused by overload due to short circuits, excessive current consumption by consumers or other errors.Defective vehicle fuses must always be replaced with vehicle fuses with the same rated current. In emergencies, use fuses with a lower rated current until the next workshop.
Automotive fuses must never be patched using "bridges" made of conductive materials. There is a risk of serious damage to the vehicle electrical system, including a cable fire!
Protect vehicle fuses and their plug connections from dirt and corrosion. Bend or replace loose or corroded contact plugs.
To protect the circuits and lines against short circuits and overloads caused by excessive current flows, fuses are used in automotive engineering. There are now a number of types of fuse on the market, although some designs are no longer used.
As a rule, fuses are used in which a metal strip integrated into the fuse melts and interrupts the circuit if an overload or a short circuit occurs.
Circuit breakers are used rarely and only for certain applications (e.g. electric windows, central locking), which use a bimetal element to interrupt the current in this circuit for a certain time in the event of overload or continuous operation.

Automotive fuses circuit symbols
The circuit symbol shown here is used for automotive fuses in electrical circuit diagrams.
Immediately next to it there is usually the legend designation of the fuse, which is always designated "F" in connection with numbers for fuses. The rated amperage is often also given in the circuit diagram.
The digits are usually dialed after the fuse number in the fuse box.
If there are several fuse boxes in the vehicle, the numbering may differ.
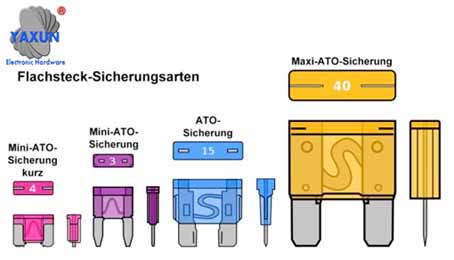
Automotive fuse types
ATO fuseThis type of fuse is mainly used to protect the electrical system in motor vehicles.
ATO means "Automotive Technology Organization".
These fuses first appeared around 1976 and are standardized according to ISO 8820-3.
The advantage of this type of fuse is the small amount of space required and the relatively wide contact tongues, which ensure reliable contact in the plug and thus keep contact resistances and thus the voltage drop in the on-board network low.
The color of the fuse body indicates the rated current.

Special form of the blade fuse
A special type of blade fuse is available in electronics stores, in which a built-in light-emitting diode lights up when the fuse has blown.
In the dark, defective fuses can be quickly identified without a lengthy search.
However, these backups are significantly more expensive than standard backups.
The vehicle manufacturer / device manufacturer can also refuse guarantee services or goodwill if the on-board network or a device is damaged without or despite the activation of such a fuse.
The following colors and gradations apply to the rated amperage of the blade terminal fuses:
| 1 A | 2 A | 3 A | 4 A | 5 A | 7,5 A | 10 A | 15 A | 20 A | 25 A | 30 A | 35 A | 40 A |
The Maxi ATO fuses are often used to protect heavy loads, the fuse boxes provided for this are usually located in the engine compartment near the vehicle battery. Rated currents of at least 20 A up to 120 A are usual for this type of fuse.
The blade fuses cannot always be easily pulled out due to their tight fit in the tongues and the limited installation space.
There is usually a plastic tool in the fuse box for pulling these fuses.
If such a tool is not available, it is advisable to provide an appropriate replacement.
 |
 |
 |
| MAXI Large Car Fuse | MINI small car fuse | Micro3 small car fuse |
ATS fuse
This fuse was mainly used on European vehicles until the 1980s.
This type of fuse is also standardized according to DIN 72581-1.
Today this type of fuse is hardly used any more, because the decreasing spring force of the retaining tabs and the small contact area between the fuse and retaining tabs often result in high contact resistances.
Other names for this type of fuse are:
Torpedo fuse
Ton fuse
Bosch fuse
With this fuse type, the rated amperage is also indicated by the uniform color of the fuse body:
| 5 A | 8 A | 16 A | 25 A | 40 A |
Automotive glass fuses
Motor vehicle glass fuses were mainly used by American and Asian motor vehicle manufacturers until the advent of ATO fuses.
Today, these glass fuses are still occasionally used as device fuses (e.g. car radio), although they have now been largely replaced by ATO fuses.
The exact type of fuse to be observed when replacing is indicated on the metal caps.
Glass fuses measuring 5 x 20 mm are common for the European market, while fuses measuring 6.3 x 32 mm are often used on the American and Asian markets.
As a rule, a maximum of 20 A rated current limit is installed for glass fuses.

ANL fuses
In relatively new vehicles in particular, ANL fuses are installed that are designed for high rated currents (usually more than 40 A).These fuses are usually housed in a fuse box next to the vehicle battery and are screwed together.
This type of fuse is also standardized according to DIN 43560 or DIN 72581.
To avoid short circuits caused by loosening tools, the battery must be disconnected before changing these fuses.
If an ANL fuse trips, it can be assumed that there is a major problem in the on-board electrical system.
A check of the on-board network by a specialist workshop is recommended to avoid further damage.

Checking fuses
Using the visible metal flags, a test lamp can be used to check whether a current is flowing through the fuse, even without pulling out the fuse.Connect the alligator clip to ground and test both contacts one after the other with the test probe.
It should be noted that not all fuses are connected directly to terminal 30 or 15.
In some cases, the lighting fuse is only energized when the light switch is actuated in the appropriate position.
The test can of course also be carried out with a commercially available multimeter.
Blown fuse
The fuse filament has blown due to an excessive current flow.
In the case of very high fault currents (massive short circuit), the plastic body of the fuse may be melted.
Insert a new fuse.
If the fuse blows again, the corresponding circuit must be checked carefully.
Safety thread broken or burned out
As a result of vibrations or a relatively slightly excessive current flow, the melt filament can in exceptional cases be barely noticeably defective.
Device failure may only occur in the event of vibrations or small consumers with low power consumption function; malfunctions only occur when larger consumers are added (e.g. radio).
Insert a new fuse.
Plug-in pins damaged by corrosion
The contact pins of the fuse can be corroded by penetrating moisture or (in the area of the battery) overcharging and the resulting acid vapors.
The contact resistance leads to a more or less strong voltage drop, larger loads may show malfunctions.
Replace fuse, remove rust from plug contacts either with fine sandpaper or replace.
PREV:Application of thermal fuse?
NEXT:NONE
NEXT:NONE





