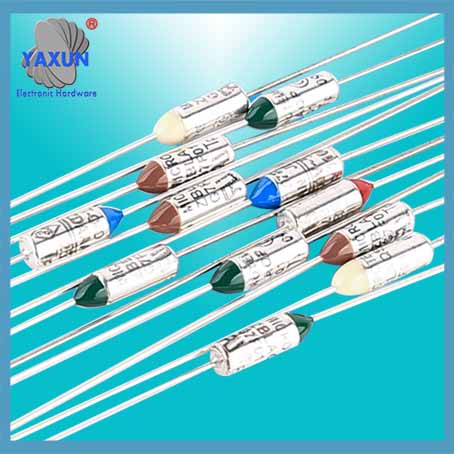
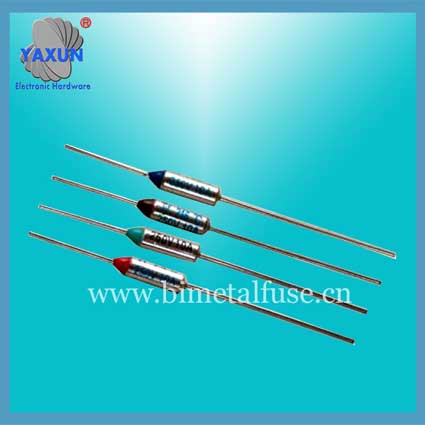
OEM Parts Ceramics High Temperature Built in Thermal Fuse
- PRODUCT DETAIL
The thermal fuse is a thermal protector. Thermal fuses are mainly composed of melts and tubes, plus external fillers. When using, connect the thermal fuse in series with the protected circuit. When the current of the protected circuit exceeds the specified value, and after a certain period of time, the melt generated by the melt itself fuses the melt, breaking the circuit, thereby protecting the circuit. Electrical appliances that use a metal conductor as a melt to break a circuit are connected in series in the circuit. When an overload or short-circuit current passes through the melt, the melt itself will heat up and melt. Therefore, it has played a certain role in protecting the power system, various electrical equipment and household appliances. With anti-delay characteristic, when the overload current is small, the fusing time is long; When the overload current is large, the fusing time is short. Therefore, within a certain range of overload current until the current returns to normal, the thermal fuse will not blow and can continue to be used. The thermal fuse is mainly composed of a melt, a housing and a support. Among them, hot melt is the key element to control the fusing characteristics.
In the import and export tariffs, they are classified as 8535 or 8536.
working principle
A metal conductor is used as a melt in series in the circuit. When an overload or short-circuit current flows through the melt, it is fused because of its own heat, thereby breaking the circuit. Thermal fuses are simple in structure and easy to use. They are widely used as protection devices in power systems, various electrical equipment and household appliances.
Features
The rated fuse current is not equal to the rated current of the fuse. The rated current of the melt is selected according to the load current of the protected equipment. The rated current of the fuse shall be greater than the rated current of the fuse, and shall be determined in cooperation with the main electrical appliance.
The thermal fuse is mainly composed of a melt, a housing and a support. Among them, the melt is the key component to control the fusing characteristics. The material, size and shape of the melt determine the fusing characteristics. Melt materials are divided into two types, low melting points and high melting points. Low-melting materials such as lead and lead alloys have low melting points and are easy to melt. Because of its large resistivity, the cross-sectional size of the melt is large, and more metal vapor is generated during melting. Only for fuses with low breaking capacity. High melting point materials such as copper and silver have high melting points and are not easy to melt. However, due to its low resistivity, it can be made smaller in cross-section size than a low melting point melt, and less metal vapor is generated during melting. Suitable for fuses with high breaking capacity. The shape of the melt is divided into two types: filament and ribbon. Changing the shape of the variable cross section can significantly change the fuse characteristics of the fuse.
Thermal fuses have anti-delay characteristics, that is, when the overload current is small, the fuse time is long; When the overload current is large, the fusing time is short. Therefore, within a certain overload current range, when the current returns to normal, the thermal fuse will not blow and can continue to be used. Thermal fuses have various different fuse characteristic curves, which can be adapted to the needs of different types of protection objects.
effect
Electrical components installed in a circuit to ensure safe operation of the circuit. When the circuit is faulty or abnormal, the current is constantly increasing, and the increased current may damage some important or valuable components in the circuit, or it may burn the circuit or even cause a fire. If the thermal fuse is correctly installed in the circuit, the thermal fuse will fuse itself to cut off the current when the current abnormally rises to a certain height and a certain time. So as to protect the safe operation of the circuit. Thermal cutoff cuts off the current, thereby protecting the safe operation of the circuit.
Inter-level cooperation
In order to prevent over-level fusing and expand the scope of the accident, there should be good coordination between the thermal fuses of the upper and lower levels (ie, power supply trunks and branch lines). When selecting, the fuse rated current of the upper stage (power supply main line) thermal fuse should be 1 to 2 stages larger than that of the lower stage (power supply branch line). Commonly used thermal fuses are tubular thermal fuses R1 series, Spiral thermal fuse RLl series, Packed closed thermal fuse RT0 series and fast thermal fuse RSO, RS3 series, etc.
Related introduction
Use and maintenance
Thermal fuse in low-voltage power distribution system is an electrical appliance that plays a role in safety protection. Thermal fuses are widely used in power grid protection and electrical equipment protection. When short circuit or overload occurs in the power grid or electrical equipment, the circuit can be automatically cut off to avoid damage to electrical equipment and prevent accidents from spreading.
Thermal fuse is composed of insulating base (or support), contacts, melt and so on. The fuse is the main working part of the fuse. The melt is equivalent to a special wire connected in series in the circuit. When the circuit is short-circuited or overloaded, the current is too large, and the melt melts due to overheating, thereby cutting off the circuit. The melt is often made into filaments, grids or flakes. Melt materials have the characteristics of low relative melting point, stable characteristics and easy melting. Generally use lead-tin alloy, silver-plated copper sheet, zinc, silver and other metals. In the process of melting and cutting off the circuit, an arc will be generated. In order to extinguish the arc safely and effectively, the melt is generally installed in the fuse housing, and measures are taken to quickly extinguish the arc.
Fuses have the advantages of simple structure, convenient use, and low price, and are widely used in low-voltage systems.
Temperature fuse Brand: TAMURA / Tamura, Albemarle, NEC, Emerson / Emerson, Emerson, Japan, Panasonic / Matsushita, Xingyu, JingKe, PANASONIC
First, the design and operation principle of a thermal fuse
● thermal fuse has detected abnormal temperature and cut off the circuit function. It can detect the temperature of household or industrial electrical products abnormal rise in temperature and quickly cut off the circuit, can be achieved to prevent the effects of fire in unburned.
● temperature fuse wire type with axial and radial lead type two. Using a thermal particles (organic matter).
● Safety Certification: UL, CSA, VDE, BEBA, PSE, JET, CQC ... certificate, EU ROHS environmental directives
● Current Product: 1A, 2A, 3A, 5A, 10A, 15A, 20A
Second, the application of various types of household appliances products; such as iron, hair dryer (hair dryer), oven, straight hair, vacuum cleaners, electric heaters, electric fans Juicers, blenders, power supplies, motors, printers, copiers, fax machine, HID ballasts, fluorescent lighting ballasts, transformers, charger, battery pack, heating appliances, electric heaters, rice cookers, electric thermos, coffee pots, ventilation fans, fans, sewing machines, water heaters, power converter , power plugs and sockets, refrigerators, air conditioners, car air conditioners, instruments, equipment, and so do overheat protection.
In the import and export tariffs, they are classified as 8535 or 8536.
working principle
A metal conductor is used as a melt in series in the circuit. When an overload or short-circuit current flows through the melt, it is fused because of its own heat, thereby breaking the circuit. Thermal fuses are simple in structure and easy to use. They are widely used as protection devices in power systems, various electrical equipment and household appliances.
Features
The rated fuse current is not equal to the rated current of the fuse. The rated current of the melt is selected according to the load current of the protected equipment. The rated current of the fuse shall be greater than the rated current of the fuse, and shall be determined in cooperation with the main electrical appliance.
The thermal fuse is mainly composed of a melt, a housing and a support. Among them, the melt is the key component to control the fusing characteristics. The material, size and shape of the melt determine the fusing characteristics. Melt materials are divided into two types, low melting points and high melting points. Low-melting materials such as lead and lead alloys have low melting points and are easy to melt. Because of its large resistivity, the cross-sectional size of the melt is large, and more metal vapor is generated during melting. Only for fuses with low breaking capacity. High melting point materials such as copper and silver have high melting points and are not easy to melt. However, due to its low resistivity, it can be made smaller in cross-section size than a low melting point melt, and less metal vapor is generated during melting. Suitable for fuses with high breaking capacity. The shape of the melt is divided into two types: filament and ribbon. Changing the shape of the variable cross section can significantly change the fuse characteristics of the fuse.
Thermal fuses have anti-delay characteristics, that is, when the overload current is small, the fuse time is long; When the overload current is large, the fusing time is short. Therefore, within a certain overload current range, when the current returns to normal, the thermal fuse will not blow and can continue to be used. Thermal fuses have various different fuse characteristic curves, which can be adapted to the needs of different types of protection objects.
effect
Electrical components installed in a circuit to ensure safe operation of the circuit. When the circuit is faulty or abnormal, the current is constantly increasing, and the increased current may damage some important or valuable components in the circuit, or it may burn the circuit or even cause a fire. If the thermal fuse is correctly installed in the circuit, the thermal fuse will fuse itself to cut off the current when the current abnormally rises to a certain height and a certain time. So as to protect the safe operation of the circuit. Thermal cutoff cuts off the current, thereby protecting the safe operation of the circuit.
Inter-level cooperation
In order to prevent over-level fusing and expand the scope of the accident, there should be good coordination between the thermal fuses of the upper and lower levels (ie, power supply trunks and branch lines). When selecting, the fuse rated current of the upper stage (power supply main line) thermal fuse should be 1 to 2 stages larger than that of the lower stage (power supply branch line). Commonly used thermal fuses are tubular thermal fuses R1 series, Spiral thermal fuse RLl series, Packed closed thermal fuse RT0 series and fast thermal fuse RSO, RS3 series, etc.
Related introduction
Use and maintenance
Thermal fuse in low-voltage power distribution system is an electrical appliance that plays a role in safety protection. Thermal fuses are widely used in power grid protection and electrical equipment protection. When short circuit or overload occurs in the power grid or electrical equipment, the circuit can be automatically cut off to avoid damage to electrical equipment and prevent accidents from spreading.
Thermal fuse is composed of insulating base (or support), contacts, melt and so on. The fuse is the main working part of the fuse. The melt is equivalent to a special wire connected in series in the circuit. When the circuit is short-circuited or overloaded, the current is too large, and the melt melts due to overheating, thereby cutting off the circuit. The melt is often made into filaments, grids or flakes. Melt materials have the characteristics of low relative melting point, stable characteristics and easy melting. Generally use lead-tin alloy, silver-plated copper sheet, zinc, silver and other metals. In the process of melting and cutting off the circuit, an arc will be generated. In order to extinguish the arc safely and effectively, the melt is generally installed in the fuse housing, and measures are taken to quickly extinguish the arc.
Fuses have the advantages of simple structure, convenient use, and low price, and are widely used in low-voltage systems.
Temperature fuse Brand: TAMURA / Tamura, Albemarle, NEC, Emerson / Emerson, Emerson, Japan, Panasonic / Matsushita, Xingyu, JingKe, PANASONIC
First, the design and operation principle of a thermal fuse
● thermal fuse has detected abnormal temperature and cut off the circuit function. It can detect the temperature of household or industrial electrical products abnormal rise in temperature and quickly cut off the circuit, can be achieved to prevent the effects of fire in unburned.
● temperature fuse wire type with axial and radial lead type two. Using a thermal particles (organic matter).
● Safety Certification: UL, CSA, VDE, BEBA, PSE, JET, CQC ... certificate, EU ROHS environmental directives
● Current Product: 1A, 2A, 3A, 5A, 10A, 15A, 20A
Second, the application of various types of household appliances products; such as iron, hair dryer (hair dryer), oven, straight hair, vacuum cleaners, electric heaters, electric fans Juicers, blenders, power supplies, motors, printers, copiers, fax machine, HID ballasts, fluorescent lighting ballasts, transformers, charger, battery pack, heating appliances, electric heaters, rice cookers, electric thermos, coffee pots, ventilation fans, fans, sewing machines, water heaters, power converter , power plugs and sockets, refrigerators, air conditioners, car air conditioners, instruments, equipment, and so do overheat protection.
|
model
|
Rated operating temperature (Tf)
|
Actual operating temperature (Ct) |
Maintaining the temperature (Th) |
Limit temperature (Tm) |
Rated voltage (Ur) |
|
RF90
|
90℃
|
86±3℃
|
55℃
|
180℃
|
250V
|
|
RF100
|
100℃
|
96±3℃
|
68℃
|
180℃
|
250V
|
|
RF110
|
110℃
|
105±3℃
|
75℃
|
180℃
|
250V
|
|
RF115
|
115℃
|
110±3℃
|
75℃
|
180℃
|
250V
|
|
RF120
|
120℃
|
116±3℃
|
85℃
|
180℃
|
250V
|
|
RF125
|
125℃
|
121±3℃
|
90℃
|
180℃
|
250V
|
|
RF130
|
130℃
|
125±3℃
|
92℃
|
180℃
|
250V
|
|
RF135
|
135℃
|
131±3℃
|
95℃
|
180℃
|
250V
|
|
RF140
|
140℃
|
136±3℃
|
100℃
|
180℃
|
250V
|
|
RF145
|
145℃
|
141±3℃
|
105℃
|
180℃
|
250V
|
|
RF150
|
150℃
|
146±3℃
|
113℃
|
180℃
|
250V
|
|
RF155
|
155℃
|
150±3℃
|
113℃
|
200℃
|
250V
|
|
RF158
|
158℃
|
155±3℃
|
113℃
|
200℃
|
250V
|
|
RF160
|
160℃
|
157±3℃
|
125℃
|
200℃
|
250V
|
|
RF165
|
165℃
|
161±3℃
|
125℃
|
200℃
|
250V
|
|
RF170
|
170℃
|
165±3℃
|
125℃
|
230℃
|
250V
|
|
RF172
|
172℃
|
167±3℃
|
135℃
|
230℃
|
250V
|
|
RF175
|
175℃
|
170±3℃
|
135℃
|
230℃
|
250V
|
|
RF180
|
180℃
|
177±3℃
|
140℃
|
230℃
|
250V
|
|
RF185
|
185℃
|
181±3℃
|
148℃
|
230℃
|
250V
|
|
RF188
|
188℃
|
184±3℃
|
148℃
|
230℃
|
250V
|
|
RF190
|
190℃
|
187±3℃
|
148℃
|
230℃
|
250V
|
|
RF192
|
192℃
|
189±3℃
|
155℃
|
230℃
|
250V
|
|
RF195
|
195℃
|
192±3℃
|
155℃
|
250℃
|
250V
|
|
RF200
|
200℃
|
197±3℃
|
160℃
|
280℃
|
250V
|
|
RF210
|
210℃
|
205±3℃
|
172℃
|
280℃
|
250V
|
|
RF216
|
216℃
|
212±3℃
|
175℃
|
280℃
|
250V
|
|
RF230
|
230℃
|
227±3℃
|
185℃
|
300℃
|
250V
|
|
RF240
|
240℃
|
235±3℃
|
190℃
|
300℃
|
250V
|
|
RF250
|
250℃
|
247±3℃
|
208℃
|
320℃
|
250V
|