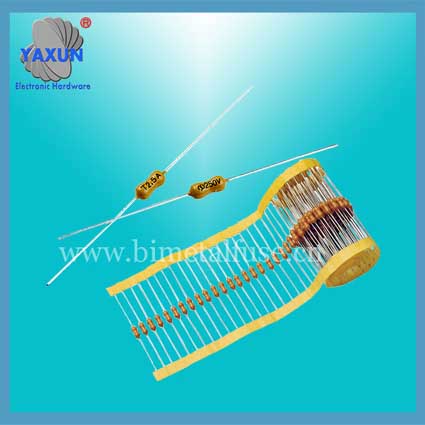
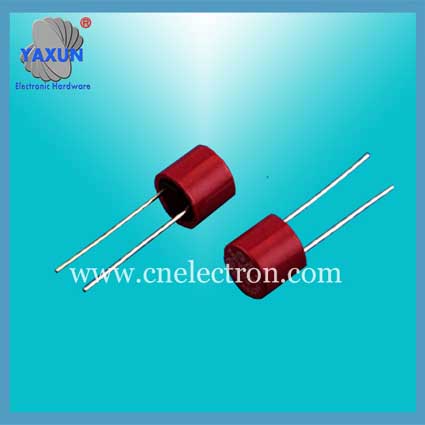
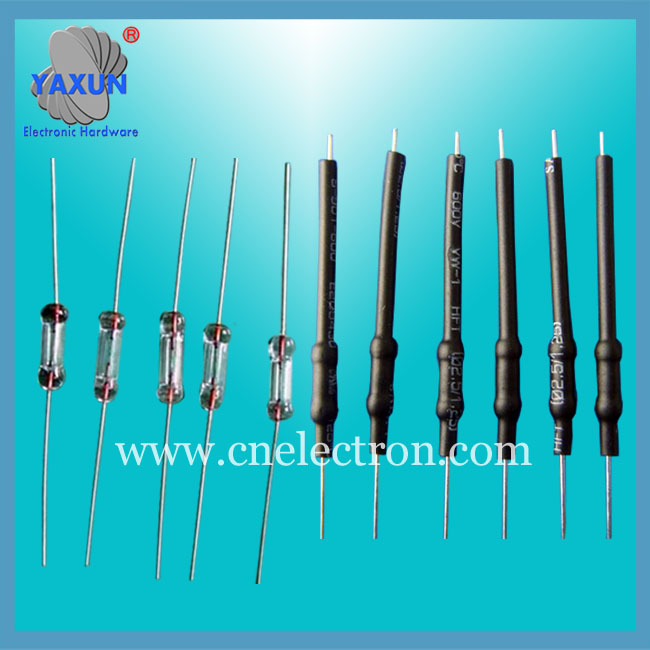
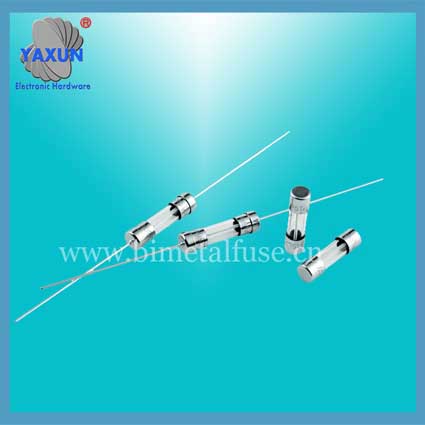
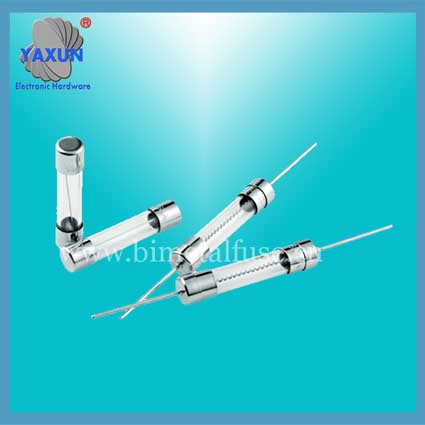
Littelfuse Circular TR5 372 382 micro fuse manufacturer
- PRODUCT DETAIL
Fuse shape
Fuse sign
Most fuses are marked on the body or with end caps and markings indicating their rating. But "chip type" fuses have little or no marking, making identification very difficult.
Fuses may exhibit similar and significantly different characteristics, identifying their markings. Fuse marking usually conveys the following information:
Ampere fuse rating
Voltage level fuse
Time-current characteristics, ie speed fuse
Approved by national and international standards bodies
Manufacturer / Product Number / Series
Fusing capacity
Intentions to develop, to use technology to benefit society
Functional Characteristics
Approvals (○ Pending ● Approvals )
1. Filiform. Earlier original types of fuses were directly screw-locked and used for old switches and sockets of various sizes.
2. Flaky (naked). Chip fuses are more convenient to use than older wire types.
3. Glass tube. There are several different sizes, common in electronics.
6.3 x 32 mm (diameter x length)
5 x 20 mm
4. Ceramic tube. There are several different shapes and sizes to prevent glass from bursting.
5, plastic sheet with metal flake pin: Automotive fuse.
6. Surface Mount Device (SMD) type.
7. Cylinder-shaped, plug-in type: directly soldered to the circuit board, used in the product.
2. Flaky (naked). Chip fuses are more convenient to use than older wire types.
3. Glass tube. There are several different sizes, common in electronics.
6.3 x 32 mm (diameter x length)
5 x 20 mm
4. Ceramic tube. There are several different shapes and sizes to prevent glass from bursting.
5, plastic sheet with metal flake pin: Automotive fuse.
6. Surface Mount Device (SMD) type.
7. Cylinder-shaped, plug-in type: directly soldered to the circuit board, used in the product.
Fuse sign
Most fuses are marked on the body or with end caps and markings indicating their rating. But "chip type" fuses have little or no marking, making identification very difficult.
Fuses may exhibit similar and significantly different characteristics, identifying their markings. Fuse marking usually conveys the following information:
Ampere fuse rating
Voltage level fuse
Time-current characteristics, ie speed fuse
Approved by national and international standards bodies
Manufacturer / Product Number / Series
Fusing capacity
Intentions to develop, to use technology to benefit society
| Breaking Capacity | Material | Operating Temperature | Soldering conditions |
|
VDE:100 amperes at 250V/300V AC(250mA-6.3A) UL:100 amperes at 125V/250V/300V/350V AC (250mA-6.3A) |
Fuse body –Plastic Element--Alloy Pigtail--tin plated copper |
-40℃~+125℃ |
Wave solder:260℃,≤5S Hand solder: 360℃,≤1S |
| Testing current | Blow Time | |
| Min | Max | |
| 150% | 1 hour | |
| 210% | 1s | 120s |
| 275% | 400ms | 10s |
| 400% | 150ms | 3ms |
| 1000% | 20ms | 150ms |
|
Current Rating |
Voltage Rating |
Norminal Melting I2T(A2sec) |
Approvals | ||||||
| VDE | CCC | CQC | UL | KC | PSE | ||||
| 250mA | 250V | 0.28 | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||
| 315mA | 250V | 0.45 | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||
| 400mA | 250V | 0.80 | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||
| 500mA | 250V | 1.2 | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||
| 630mA | 250V | 1.8 | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||
| 800mA | 250V | 3.0 | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||
| 1A | 250V | 4.2 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ○ | ||
| 1.25A | 250V | 5.0 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ○ | ||
| 1.6A | 250V | 8.2 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ○ | ||
| 2A | 250V | 9.8 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ○ | ||
| 2.5A | 250V | 16.0 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ○ | ||
| 3.15A | 250V | 22.5 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ○ | ||
| 4A | 250V | 30.0 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ○ | ||
| 5A | 250V | 64.0 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ○ | ||
| 6.3A | 250V | 72.0 | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||
| 7A | 250V | 125 | ○ | ||||||
| 8A | 250V | 164 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||
| 10A | 250V | 256 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||