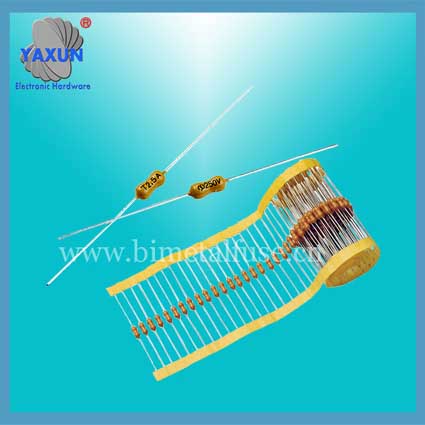
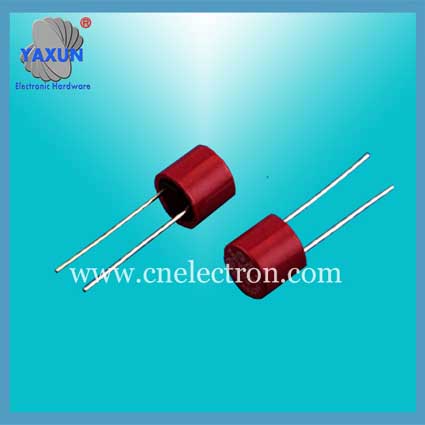
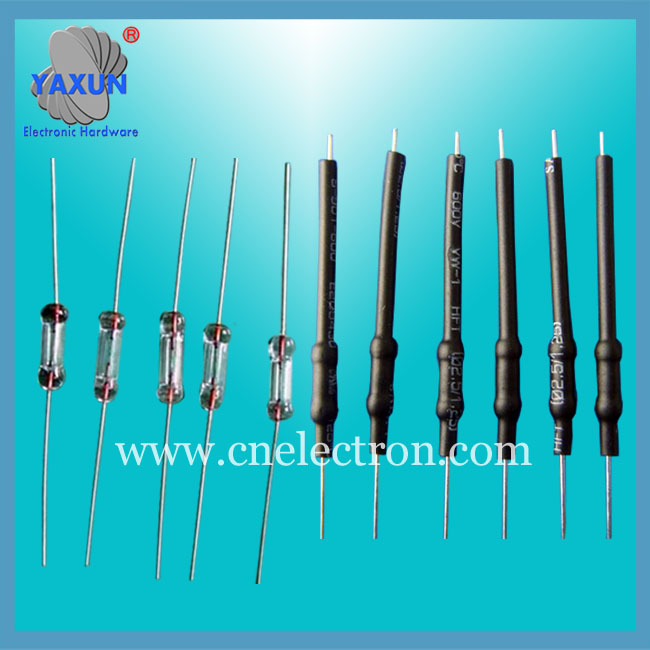
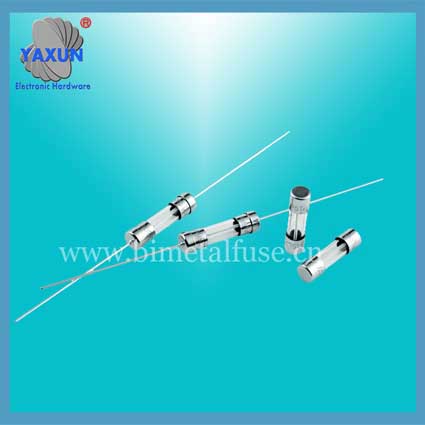
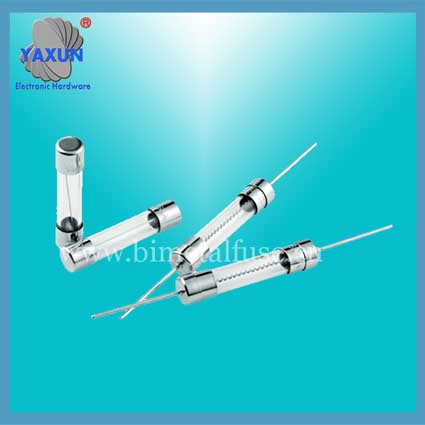
Φ2.4x7、5x20mm FST Miniature Glass Tube Fast Blown Cartridge Fuses
- PRODUCT DETAIL
Fuse Application Notes
1. The normal operating current is operated at 25 ° C, and the current rating of the fuse is usually reduced by 25% to avoid harmful melting. Most traditional fuses use a material with a lower melting temperature. Therefore, this fuse is more sensitive to changes in ambient temperature. For example, a fuse with a current rating of 10A is generally not recommended to operate at a current greater than 7.5A at an ambient temperature of 25 ° C.
2. Voltage Rating The voltage rating of the fuse must be equal to or greater than the effective circuit voltage. The general standard voltage rating series are 32V, 125V, 250V, 600V.
3. The resistance of a resistance fuse is not important throughout the circuit. Because the fuse resistance of amperage less than 1A is only a few ohms, this issue should be considered when using fuses in low voltage circuits. Most fuses are made of materials with a positive temperature coefficient, so there is a distinction between cold and thermal resistance.
4. The experiment of the current carrying capacity of the ambient temperature fuse is carried out under the ambient temperature of 25 ° C. This experiment is affected by the change of the ambient temperature. The higher the ambient temperature, the higher the operating temperature of the fuse and the shorter its life. Conversely, operating at lower temperatures will extend the life of the fuse.
5. Fuse rated capacity of the breaking capacity is also referred to. The rated fuse capacity is the maximum allowable current that a fuse can blow at the rated voltage. In the event of a short circuit, the fuse will pass multiple instantaneous overload currents greater than the normal operating current. Safe operation requires the fuse to remain intact (no bursts or breaks) and eliminate short circuits.
Intentions to develop, to use technology to benefit society
Functional Characteristics
Approvals (○ Pending ● Approvals )
1. The normal operating current is operated at 25 ° C, and the current rating of the fuse is usually reduced by 25% to avoid harmful melting. Most traditional fuses use a material with a lower melting temperature. Therefore, this fuse is more sensitive to changes in ambient temperature. For example, a fuse with a current rating of 10A is generally not recommended to operate at a current greater than 7.5A at an ambient temperature of 25 ° C.
2. Voltage Rating The voltage rating of the fuse must be equal to or greater than the effective circuit voltage. The general standard voltage rating series are 32V, 125V, 250V, 600V.
3. The resistance of a resistance fuse is not important throughout the circuit. Because the fuse resistance of amperage less than 1A is only a few ohms, this issue should be considered when using fuses in low voltage circuits. Most fuses are made of materials with a positive temperature coefficient, so there is a distinction between cold and thermal resistance.
4. The experiment of the current carrying capacity of the ambient temperature fuse is carried out under the ambient temperature of 25 ° C. This experiment is affected by the change of the ambient temperature. The higher the ambient temperature, the higher the operating temperature of the fuse and the shorter its life. Conversely, operating at lower temperatures will extend the life of the fuse.
5. Fuse rated capacity of the breaking capacity is also referred to. The rated fuse capacity is the maximum allowable current that a fuse can blow at the rated voltage. In the event of a short circuit, the fuse will pass multiple instantaneous overload currents greater than the normal operating current. Safe operation requires the fuse to remain intact (no bursts or breaks) and eliminate short circuits.
Intentions to develop, to use technology to benefit society
| Breaking Capacity | Material | Operating Temperature | Soldering conditions |
| 50 amperes at 125V/250V AC (250mA - 10A) |
Fuse body – Glass tube End cap-- nickel plated brass Pigtail -- tin plated copper on nickel plated brass cap |
-40℃~+125℃ |
Wave solder:260℃,≤5S Hand solder: 360℃,≤1S |
| Testing current | Blow Time | |
| Min最小 | Max | |
| 100% | 4 hour | - |
| 200% | 100ms | 60 s |
Approvals (○ Pending ● Approvals )
| Current Rating |
Voltage Rating |
Norminal Melting I2T(A2sec) |
Approvals | |
| UL | ||||
| 200mA | 125V/250V | 0.06 | ● | |
| 250mA | 125V/250V | 0.10 | ● | |
| 300mA | 125V/250V | 0.12 | ● | |
| 315mA | 125V/250V | 0.14 | ● | |
| 350mA | 125V/250V | 0.18 | ● | |
| 400mA | 125V/250V | 0.23 | ● | |
| 500mA | 125V/250V | 0.38 | ● | |
| 600mA | 125V/250V | 0.41 | ● | |
| 630mA | 125V/250V | 0.42 | ● | |
| 750mA | 125V/250V | 0.47 | ● | |
| 800mA | 125V/250V | 0.53 | ● | |
| 1A | 125V/250V | 0.65 | ● | |
| 1.25A | 125V/250V | 1.25 | ● | |
| 1.5A | 125V/250V | 2.2 | ● | |
| 2A | 125V/250V | 4.1 | ● | |
| 2.5A | 125V/250V | 7.2 | ● | |
| 3A | 125V/250V | 14 | ● | |
| 3.15A | 125V/250V | 17 | ● | |
| 3.5A | 125V/250V | 18 | ● | |
| 4A | 125V/250V | 19 | ● | |
| 5A | 125V/250V | 22 | ● | |
| 6A | 125V/250V | 25 | ● | |
| 6.3A | 125V/250V | 28.8 | ● | |