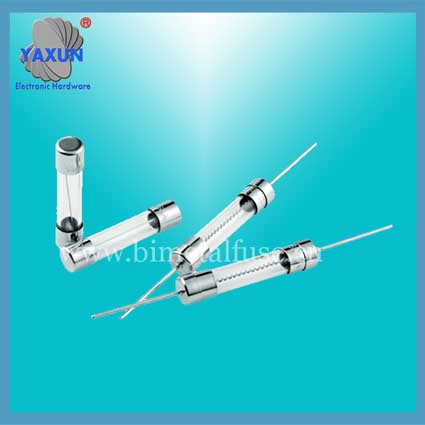
China electronics and electrical Fuse Manufacturers
- PRODUCT DETAIL
Fuse Manufacturing
Ya Xun focus on the new over-current | overheating electronic protection components of the research, development, manufacturing and sales, access to a number of world-class fuse patent, with over-current protection alloy wire and overheating protection of fusible alloy wire and other advanced technology, using German automated production process. Provide a full range of current fuses, thermal fuses and other products, high performance, reliability, electronic circuit protection is the best choice.
Ya Xun for domestic and foreign customers with professional free design and application services, and to quickly deliver, excellent cost-effective to win customers praise. Ya Xun has a complete engineering research and development center,
Is the world with a small number of industry at the same time have the materials, equipment, technology patents, as well as computer simulation technology, mechanical and electrical integration R & D strength of the company, manufacturing efficiency, protection of electronic components in the field of world leader.
Our engineers combine the advanced technology of fuses and thermal fuses with traditional industrial technology, to provide you with one-stop from the rapid proofing to small batch production services. Please contact our professional team, let us come for you to achieve all the technical requirements.
What Is A Fuse?
Fuses are also known as current fuses, and the IEC127 standard defines it as a "fuse body." It is primarily a function of current overload protection. When the circuit fails or abnormal, accompanied by rising current, and the rising current may damage some important devices in the circuit, it is possible to burn the circuit or even cause a fire.
If the circuit correctly install the fuse, then the fuse will rise in the current to a certain height and heat, when the fuse itself cut off the current, so as to protect the safe operation of the circuit.
Fuse Characteristics
• Resistivity is large; low melting point.
• Small size, easy to install
• Disjunction capability precision, reliability
• Different structural features, installation in various forms
• Under normal conditions, the fuse has a long shelf life
• Recoverable fuse, reset can be repeated use
• Long life of the fuse, in case of fault-free circuit, synchronized with the life of the equipment

Working Principle
Current fuse is a hot fusing working principle, when the current flows through the conductor, because fusing wire conductor there is a certain resistance, so the conductor will heat up. When the circuit current is not normal rise,fusing wire will heat fusing, cut off the circuit current.
Resettable fuse is a current anomaly, the resistance becomes larger working principle, when the current through the polymer polymer is not normal rise, the fuse resistance will become larger, through the fuse current will be reduced to ensure the normal work of the circuit.
Fuse Classification
Scope of use: power fuses, machine fuses, electronic fuses, car fuses.
Volume classification: large, medium, small and micro (SMD type).
Rated voltage classification: high voltage fuses, low voltage fuses and safety voltage fuses.
Breaking capacity classification: high and low breaking capacity fuse.
Shape classification:
Flat head tube fuse (can be divided into internal welding fuse and external welding fuse), Online fuses (Single hat online and double hat online, live), Punched Fuse, Guillotine Fuse, Screw Fuse, Insert Fuse, Flat Fuse, Wrap Fuse, SMD Fuse, Resistive Fuse.
Fusing speed (symbol) Category:
(Usually with the TT said), Slow fuse (generally used T), medium-speed fuse (generally used M), fast break fuse (generally used F said), special fast fuse (usually with FF) The
According to the current classification: 32ma, 63ma, 100mA, 150mA, 200mA, 250mA, 300mA, 400mA, 500mA, 600mA, 800mA, 1A, 1.25A,1.6A, 2A, 2.5A, 3A, 3.5A, 4A, 5A, 6A, 7A, 8A, 9A, 10A, 12A, 15A, 20A, 25A, 30A
Material points can be divided into: lead antimony alloy wire, lead-tin synthetic wire, silver-copper alloy wire, polymer PTC
 Fuse Selection
Fuse Selection
The most commonly used in circuit overcurrent protection components is the fuse. It is usually in series in the circuit, the fault current increases to a certain value, its own fusing and cut off the circuit, to protect the circuit in other equipment. So it is important to choose a suitable fuse:
A) Safety standards: European regulations fuse, the United States regulatory fuse, the Japanese regulatory fuse
B) Dimensions.
C) Fusing type: According to the current characteristics of the protected circuit, select the fuse fuse type (such as fast break F, slow cut T). For example, the current characteristic of the protected circuit is constant current, then fast fuse type is used.
D) Rated voltage (Un): nominal operating voltage of the fuse, code is Un, the fuse voltage rating must be equal to or greater than the effective circuit voltage. General standard voltage rating series is 32V, 125V, 250V, 600V.
F) Fuse minimum I2T : Determine the I2T of the fuse according to the surge I2T of the protected circuit. For example, the surge circuit I2T is 1 (A2S), in order to ensure that the fuse can withstand more than 100,000 times the impact of the fuse I2T should be greater than: ÷ 0.2 = 5 (A2S).
G) Rated current (In): also known as the nominal operating current of the fuse, code is In, the rated current of the fuse is determined by the manufacturing department in the laboratory conditions.
The structure and installation of the fuse
Current fuse composition structure:
1, the melt part (ie, current protection fuse), it is the core of the fuse;
2, the electrode part, usually there are two, it is fusing wire and circuit connection important parts, it must have good conductivity, can not produce a significant installation contact resistance;
3, the housing bracket portion:
Fusing wire are generally slender and soft, the role of the bracket is fusing wire fixed into a rigid product, easy to install.
Resettable fuse composition structure:
1, polymer and conductive carbon particles, which is the core of current protection. When the current is not normal increase, the polymer temperature will rise, the resistance increases sharply by several orders of magnitude, reducing the current through the circuit to protect the circuit safety;
2, sealed shell, high molecular polymer and conductive carbon particles is a powder mixture, sealing material must consider the product's thermal function and easy installation, choose modified epoxy resin polyethylene packaging materials, is to consider the impact of the package on the thermal characteristics of Resettable fuse, the encapsulation layer affects the heat dissipation capacity of the core material,
When the current is large enough, the package has little effect on the operation time of the fuse, when the current through the smaller, encapsulation layer at 120 ℃ (polyethylene melting point) under the fuse of the package layer and the core material between the existence of a certain gap, the core heat dissipation capacity is poor,
Action time shorter. Therefore, the fuse package should be at the maximum thermal expansion of the core material to carry out.
(1) Tubular fuses: glass tube, ceramic tube, filled with fine quartz sand fuse, internal welding and external welding; inline fuse.
(2) Micro Fuse: resistive, transistor type, film type, plastic (cylindrical, square)
(3) Automotive fuses: Blade, bolt type, seal type, alarm type,
(4) SMD Fuse: 0402,0603,0805,1206,1210,1812,2920
(4) Fusing wire structure: round wire, flat yarn, monofilaments, twin wire, composite wire, straight, wavy, zigzag, winding wire, solder balls plus
(5) Resettable fuse: plug-in, laminated, patch
2) Installation form
(1) Panel mount + fuse box,
(2) Fuse clip installation fuse,
(3) Printed circuit board installation plug-in installation, patch installation (wave soldering): radial lead, axial lead surface mount (infrared welding):
(4) hanging installation: with fuse sets.
The Main Parameters Of The Fuse
1. Rated current (In) - The rated current of the fuse is its nominal rated current, usually refers to the circuit can work long-term maximum current value.
2. Rated voltage (U) - The rated voltage of the fuse is its nominal voltage, usually the maximum voltage that the fuse can withstand after it is disconnected.
 3. Working Temperature:
3. Working Temperature:
The operating ambient temperature or known operating temperature has a direct effect on the operation of the fuse. The higher the temperature, the hotter the fuse during operation, the shorter the life expectancy.
4. Voltage drop / cold resistance - (Ud / R) -,
In general, the fuse resistance is inversely proportional to its rated current value. In the protection circuit requires the fuse the smaller the better resistance, so that its loss of power is also small. Therefore, the provisions of its maximum voltage drop in the value of the fuse parameter.
5. Time-current characteristics - I-T characteristics or sonic characteristics
When the current flowing through the fuse exceeds the rated current, the melt temperature gradually increases, and even the final blow, which is the consequences of overload conditions.
UL The maximum fuse current of the fuse is 110% In;
IEC Specifications The maximum fusible current of the fuse is 150% In or 120% In.
6. Breaking capacity - Ir
Breaking capacity is the most important safety indicators of the fuse. it indicates the maximum current at which the fuse can safely cut off under the specified voltage. the breaking capacity is also known as the maximum breaking capacity, short-circuit breaking capacity or maximum breaking current.
When the flow through the fuse is quite large or even short circuit, still require the fuse can safely break the circuit, and does not bring any destructive.
Rated breaking capacity of fuses under 250V conditions
7. Melting Thermal Energy - (It)
1) Instantaneous current and pulse
The internal instantaneous current is derived from the switching operation of the capacitive and inductive energy storage elements in the protected circuit. External instantaneous current is derived outside, the same as the surge injection system, the duration is very short into the current.
Instantaneous current of less than 10ms is called pulse current, the pulse is harmful, it may damage the fuse and cause the fuse to fail. in most cases, the delay fuse is best suited for circuit protection with pulses.
2) It value
It value is directly measured energy value needed to blow the fuse,
And the total amount: It (iterate it) = melt it + fly solitary it
8. Durability - life
The life of the fuse is very long and can be synchronized with the life of the device in the absence of a fault.
Test the IEC fuse for the life of a small fuse:
In the DC power supply conditions, the 1.20In (or 1.05In) current conduction 1h, open the opening 15min, continuous 100 cycles, and finally to 1.5 In (or 1.05In) current through 1h, during which there can not be blown or otherb phenomenon.

Ya Xun focus on the new over-current | overheating electronic protection components of the research, development, manufacturing and sales, access to a number of world-class fuse patent, with over-current protection alloy wire and overheating protection of fusible alloy wire and other advanced technology, using German automated production process. Provide a full range of current fuses, thermal fuses and other products, high performance, reliability, electronic circuit protection is the best choice.
Ya Xun for domestic and foreign customers with professional free design and application services, and to quickly deliver, excellent cost-effective to win customers praise. Ya Xun has a complete engineering research and development center,
Is the world with a small number of industry at the same time have the materials, equipment, technology patents, as well as computer simulation technology, mechanical and electrical integration R & D strength of the company, manufacturing efficiency, protection of electronic components in the field of world leader.
Our engineers combine the advanced technology of fuses and thermal fuses with traditional industrial technology, to provide you with one-stop from the rapid proofing to small batch production services. Please contact our professional team, let us come for you to achieve all the technical requirements.
What Is A Fuse?

Fuses are also known as current fuses, and the IEC127 standard defines it as a "fuse body." It is primarily a function of current overload protection. When the circuit fails or abnormal, accompanied by rising current, and the rising current may damage some important devices in the circuit, it is possible to burn the circuit or even cause a fire.
If the circuit correctly install the fuse, then the fuse will rise in the current to a certain height and heat, when the fuse itself cut off the current, so as to protect the safe operation of the circuit.
Fuse Characteristics
• Resistivity is large; low melting point.
• Small size, easy to install
• Disjunction capability precision, reliability
• Different structural features, installation in various forms
• Under normal conditions, the fuse has a long shelf life
• Recoverable fuse, reset can be repeated use
• Long life of the fuse, in case of fault-free circuit, synchronized with the life of the equipment

Working Principle

Current fuse is a hot fusing working principle, when the current flows through the conductor, because fusing wire conductor there is a certain resistance, so the conductor will heat up. When the circuit current is not normal rise,fusing wire will heat fusing, cut off the circuit current.
Resettable fuse is a current anomaly, the resistance becomes larger working principle, when the current through the polymer polymer is not normal rise, the fuse resistance will become larger, through the fuse current will be reduced to ensure the normal work of the circuit.
Fuse Classification

Scope of use: power fuses, machine fuses, electronic fuses, car fuses.
Volume classification: large, medium, small and micro (SMD type).
Rated voltage classification: high voltage fuses, low voltage fuses and safety voltage fuses.
Breaking capacity classification: high and low breaking capacity fuse.
Shape classification:
Flat head tube fuse (can be divided into internal welding fuse and external welding fuse), Online fuses (Single hat online and double hat online, live), Punched Fuse, Guillotine Fuse, Screw Fuse, Insert Fuse, Flat Fuse, Wrap Fuse, SMD Fuse, Resistive Fuse.
Fusing speed (symbol) Category:
(Usually with the TT said), Slow fuse (generally used T), medium-speed fuse (generally used M), fast break fuse (generally used F said), special fast fuse (usually with FF) The
According to the current classification: 32ma, 63ma, 100mA, 150mA, 200mA, 250mA, 300mA, 400mA, 500mA, 600mA, 800mA, 1A, 1.25A,1.6A, 2A, 2.5A, 3A, 3.5A, 4A, 5A, 6A, 7A, 8A, 9A, 10A, 12A, 15A, 20A, 25A, 30A
Material points can be divided into: lead antimony alloy wire, lead-tin synthetic wire, silver-copper alloy wire, polymer PTC
 Fuse Selection
Fuse SelectionThe most commonly used in circuit overcurrent protection components is the fuse. It is usually in series in the circuit, the fault current increases to a certain value, its own fusing and cut off the circuit, to protect the circuit in other equipment. So it is important to choose a suitable fuse:
A) Safety standards: European regulations fuse, the United States regulatory fuse, the Japanese regulatory fuse
B) Dimensions.
C) Fusing type: According to the current characteristics of the protected circuit, select the fuse fuse type (such as fast break F, slow cut T). For example, the current characteristic of the protected circuit is constant current, then fast fuse type is used.
D) Rated voltage (Un): nominal operating voltage of the fuse, code is Un, the fuse voltage rating must be equal to or greater than the effective circuit voltage. General standard voltage rating series is 32V, 125V, 250V, 600V.
F) Fuse minimum I2T : Determine the I2T of the fuse according to the surge I2T of the protected circuit. For example, the surge circuit I2T is 1 (A2S), in order to ensure that the fuse can withstand more than 100,000 times the impact of the fuse I2T should be greater than: ÷ 0.2 = 5 (A2S).
G) Rated current (In): also known as the nominal operating current of the fuse, code is In, the rated current of the fuse is determined by the manufacturing department in the laboratory conditions.
The structure and installation of the fuse

Current fuse composition structure:
1, the melt part (ie, current protection fuse), it is the core of the fuse;
2, the electrode part, usually there are two, it is fusing wire and circuit connection important parts, it must have good conductivity, can not produce a significant installation contact resistance;
3, the housing bracket portion:
Fusing wire are generally slender and soft, the role of the bracket is fusing wire fixed into a rigid product, easy to install.
Resettable fuse composition structure:
1, polymer and conductive carbon particles, which is the core of current protection. When the current is not normal increase, the polymer temperature will rise, the resistance increases sharply by several orders of magnitude, reducing the current through the circuit to protect the circuit safety;
2, sealed shell, high molecular polymer and conductive carbon particles is a powder mixture, sealing material must consider the product's thermal function and easy installation, choose modified epoxy resin polyethylene packaging materials, is to consider the impact of the package on the thermal characteristics of Resettable fuse, the encapsulation layer affects the heat dissipation capacity of the core material,
When the current is large enough, the package has little effect on the operation time of the fuse, when the current through the smaller, encapsulation layer at 120 ℃ (polyethylene melting point) under the fuse of the package layer and the core material between the existence of a certain gap, the core heat dissipation capacity is poor,
Action time shorter. Therefore, the fuse package should be at the maximum thermal expansion of the core material to carry out.
(1) Tubular fuses: glass tube, ceramic tube, filled with fine quartz sand fuse, internal welding and external welding; inline fuse.
(2) Micro Fuse: resistive, transistor type, film type, plastic (cylindrical, square)
(3) Automotive fuses: Blade, bolt type, seal type, alarm type,
(4) SMD Fuse: 0402,0603,0805,1206,1210,1812,2920
(4) Fusing wire structure: round wire, flat yarn, monofilaments, twin wire, composite wire, straight, wavy, zigzag, winding wire, solder balls plus
(5) Resettable fuse: plug-in, laminated, patch
2) Installation form
(1) Panel mount + fuse box,
(2) Fuse clip installation fuse,
(3) Printed circuit board installation plug-in installation, patch installation (wave soldering): radial lead, axial lead surface mount (infrared welding):
(4) hanging installation: with fuse sets.
The Main Parameters Of The Fuse
1. Rated current (In) - The rated current of the fuse is its nominal rated current, usually refers to the circuit can work long-term maximum current value.
2. Rated voltage (U) - The rated voltage of the fuse is its nominal voltage, usually the maximum voltage that the fuse can withstand after it is disconnected.
| Current Rating | Voltage Rating |
Norminal Melting I2T(A2sec) |
Approvals | ||
| UL | CUS | PSE | |||
| 250mA | 125V/250V | 0.25 | ● | ||
| 300mA | 125V/250V | 0.27 | ● | ||
| 315mA | 125V/250V | 0.30 | ● | ||
| 350mA | 125V/250V | 0.32 | ● | ||
| 400mA | 125V/250V | 0.45 | ● | ||
| 500mA | 125V/250V | 0.48 | ● | ||
| 600mA | 125V/250V | 0.6 | ● | ||
| 630mA | 125V/250V | 0.8 | ● | ||
| 750mA | 125V/250V | 1.0 | ● | ||
| 1A | 125V/250V | 1.8 | ● | ● | |
| 1.25A | 125V/250V | 2.2 | ● | ● | |
| 1.5A | 125V/250V | 3.1 | ● | ● | |
| 1.6A | 125V/250V | 3.5 | ● | ● | |
| 2A | 125V/250V | 5.0 | ● | ● | |
| 2.5A | 125V/250V | 7.5 | ● | ● | |
| 3A | 125V/250V | 12.5 | ● | ● | |
| 3.15A | 125V/250V | 14.2 | ● | ● | |
| 3.5A | 125V/250V | 15 | ● | ● | |
| 4A | 125V/250V | 30 | ● | ● | |
| 5A | 125V/250V | 42 | ● | ● | |
| 6A | 125V/250V | 60 | ● | ● | |
| 6.3A | 125V/250V | 68 | ● | ● | |
| 7A | 125V/250V | 82 | ● | ● | |
| 8A | 125V/250V | 95 | ● | ● | |
| 10A | 125V/250V | 107 | ● | ● | |
| 12A | 125V/250V | 115 | ● | ● | ● |
| 15A | 125V/250V | 180 | ● | ● | ● |
| 20A | 125V/250V | 576 | ● | ● | ● |
 3. Working Temperature:
3. Working Temperature:The operating ambient temperature or known operating temperature has a direct effect on the operation of the fuse. The higher the temperature, the hotter the fuse during operation, the shorter the life expectancy.
4. Voltage drop / cold resistance - (Ud / R) -,
In general, the fuse resistance is inversely proportional to its rated current value. In the protection circuit requires the fuse the smaller the better resistance, so that its loss of power is also small. Therefore, the provisions of its maximum voltage drop in the value of the fuse parameter.
5. Time-current characteristics - I-T characteristics or sonic characteristics
When the current flowing through the fuse exceeds the rated current, the melt temperature gradually increases, and even the final blow, which is the consequences of overload conditions.
UL The maximum fuse current of the fuse is 110% In;
IEC Specifications The maximum fusible current of the fuse is 150% In or 120% In.
6. Breaking capacity - Ir
Breaking capacity is the most important safety indicators of the fuse. it indicates the maximum current at which the fuse can safely cut off under the specified voltage. the breaking capacity is also known as the maximum breaking capacity, short-circuit breaking capacity or maximum breaking current.
When the flow through the fuse is quite large or even short circuit, still require the fuse can safely break the circuit, and does not bring any destructive.
| Breaking Capacity | Material | Operating Temperature | Soldering conditions |
|
10000 amperes at 125V AC (250mA-20A) 35 amperes at 250V AC (0-1A) 100 amperes at 250V AC (1.1A-3.5A) 200 amperes at 250V AC (3.6A-20A) |
Fuse body – glass/ceramic tube End cap--nickel plated brass |
-40℃~+125℃ |
Wave solder:260℃,≤5S Hand solder: 360℃,≤1S |
Rated breaking capacity of fuses under 250V conditions
| Fuse rated current | Rated breaking capacity |
| 0 A~1 A | 35 A |
| 1.1 A~3.5 A | 100 A |
| 3.6 A~19 A | 200 A |
| 10.1 A~15 A | 750 A |
| 15.1 A~30 A | 1500 A |
7. Melting Thermal Energy - (It)

1) Instantaneous current and pulse
The internal instantaneous current is derived from the switching operation of the capacitive and inductive energy storage elements in the protected circuit. External instantaneous current is derived outside, the same as the surge injection system, the duration is very short into the current.
Instantaneous current of less than 10ms is called pulse current, the pulse is harmful, it may damage the fuse and cause the fuse to fail. in most cases, the delay fuse is best suited for circuit protection with pulses.
2) It value
It value is directly measured energy value needed to blow the fuse,
And the total amount: It (iterate it) = melt it + fly solitary it
8. Durability - life
The life of the fuse is very long and can be synchronized with the life of the device in the absence of a fault.
Test the IEC fuse for the life of a small fuse:
In the DC power supply conditions, the 1.20In (or 1.05In) current conduction 1h, open the opening 15min, continuous 100 cycles, and finally to 1.5 In (or 1.05In) current through 1h, during which there can not be blown or otherb phenomenon.